1、Fragment家族常用的API
Fragment常用的三个类:
android.app.Fragment 主要用于定义Fragment
android.app.FragmentManager 主要用于在Activity中操作Fragment
android.app.FragmentTransaction 保证一些列Fragment操作的原子性,熟悉事务这个词,一定能明白~
a、获取FragmentManage的方式:
getFragmentManager() // v4中,getSupportFragmentManager
b、主要的操作都是FragmentTransaction的方法
FragmentTransaction transaction = fm.benginTransatcion();//开启一个事务
transaction.add()
往Activity中添加一个Fragment
transaction.remove()
从Activity中移除一个Fragment,如果被移除的Fragment没有添加到回退栈(回退栈后面会详细说),这个Fragment实例将会被销毁。
transaction.replace()
使用另一个Fragment替换当前的,实际上就是remove()然后add()的合体~
transaction.hide()
隐藏当前的Fragment,仅仅是设为不可见,并不会销毁
transaction.show()
显示之前隐藏的Fragment
detach()
会将view从UI中移除,和remove()不同,此时fragment的状态依然由FragmentManager维护。
attach()
重建view视图,附加到UI上并显示。
transatcion.commit()//提交一个事务
注意:常用Fragment的哥们,可能会经常遇到这样Activity状态不一致:State loss这样的错误。主要是因为:commit方法一定要在Activity.onSaveInstance()之前调用。
上述,基本是操作Fragment的所有的方式了,在一个事务开启到提交可以进行多个的添加、移除、替换等操作。
值得注意的是:如果你喜欢使用Fragment,一定要清楚这些方法,哪个会销毁视图,哪个会销毁实例,哪个仅仅只是隐藏,这样才能更好的使用它们。
a、比如:我在FragmentA中的EditText填了一些数据,当切换到FragmentB时,如果希望会到A还能看到数据,则适合你的就是hide和show;也就是说,希望保留用户操作的面板,你可以使用hide和show,当然了不要使劲在那new实例,进行下非null判断。
b、再比如:我不希望保留用户操作,你可以使用remove(),然后add();或者使用replace()这个和remove,add是相同的效果。
c、remove和detach有一点细微的区别,在不考虑回退栈的情况下,remove会销毁整个Fragment实例,而detach则只是销毁其视图结构,实例并不会被销毁。那么二者怎么取舍使用呢?如果你的当前Activity一直存在,那么在不希望保留用户操作的时候,你可以优先使用detach。
上述已经介绍完成了Fragment常用的一些方法,相信看完,大家一定清楚了Fragment的产生理由,以及如何使用Fragment,再根据API的讲解,也能明白,曾经为何觉得Fragment会出现一些列乱七八槽的问题,终究是因为没有弄清楚其生命周期。
2.实现fragment的两种方式:
a.静态实现,即在XML中声明fragment,如下:
Activity的布局文件:
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent" >
- <fragment
- android:id="@+id/id_fragment_title"
- android:name="com.zhy.zhy_fragments.TitleFragment"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="45dp" />
- <fragment
- android:layout_below="@id/id_fragment_title"
- android:id="@+id/id_fragment_content"
- android:name="com.zhy.zhy_fragments.ContentFragment"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
- </RelativeLayout>
b.动态添加,即在布局文件中声明一个位置留给fragment用,利用该位置的ID来添加或者替换该位置来完成动态的添加fragment
-
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent" >
- <fragment
- android:id="@+id/id_fragment_title"
- android:name="com.zhy.zhy_fragments.TitleFragment"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="45dp" />
- <include
- android:id="@+id/id_ly_bottombar"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="55dp"
- android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
- layout="@layout/bottombar" />
- <FrameLayout
- android:id="@+id/id_content"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:layout_above="@id/id_ly_bottombar"
- android:layout_below="@id/id_fragment_title" />
- </RelativeLayout>
然后利用fragmenttransaction的add或者replace(int ID, Fragment fragment)来完成添加的功能.
- package com.zhy.zhy_fragments;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.app.FragmentManager;
- import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
- import android.view.Window;
- import android.widget.LinearLayout;
- public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener
- {
- private LinearLayout mTabWeixin;
- private LinearLayout mTabFriend;
- private ContentFragment mWeixin;
- private FriendFragment mFriend;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
- {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- // 初始化控件和声明事件
- mTabWeixin = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.tab_bottom_weixin);
- mTabFriend = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.tab_bottom_friend);
- mTabWeixin.setOnClickListener(this);
- mTabFriend.setOnClickListener(this);
- // 设置默认的Fragment
- setDefaultFragment();
- }
- private void setDefaultFragment()
- {
- FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager();
- FragmentTransaction transaction = fm.beginTransaction();
- mWeixin = new ContentFragment();
- transaction.replace(R.id.id_content, mWeixin);
- transaction.commit();
- }
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v)
- {
- FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager();
- // 开启Fragment事务
- FragmentTransaction transaction = fm.beginTransaction();
- switch (v.getId())
- {
- case R.id.tab_bottom_weixin:
- if (mWeixin == null)
- {
- mWeixin = new ContentFragment();
- }
- // 使用当前Fragment的布局替代id_content的控件
- transaction.replace(R.id.id_content, mWeixin);
- break;
- case R.id.tab_bottom_friend:
- if (mFriend == null)
- {
- mFriend = new FriendFragment();
- }
- transaction.replace(R.id.id_content, mFriend);
- break;
- }
- // transaction.addToBackStack();
- // 事务提交
- transaction.commit();
- }
-
}
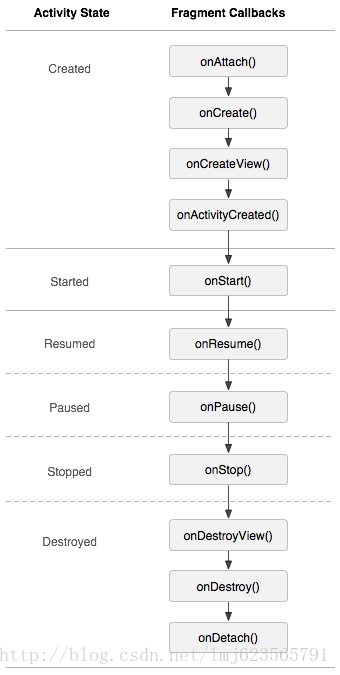
3.Fragment的生命周期
Fragment必须是依存与Activity而存在的,因此Activity的生命周期会直接影响到Fragment的生命周期。官网这张图很好的说明了两者生命周期的关系:
可以看到Fragment比Activity多了几个额外的生命周期回调方法:
onAttach(Activity)当Fragment与Activity发生关联时调用。onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup,Bundle)创建该Fragment的视图onActivityCreated(Bundle)当Activity的onCreate方法返回时调用onDestoryView()与onCreateView想对应,当该Fragment的视图被移除时调用onDetach()与onAttach相对应,当Fragment与Activity关联被取消时调用注意:除了onCreateView,其他的所有方法如果你重写了,必须调用父类对于该方法的实现,